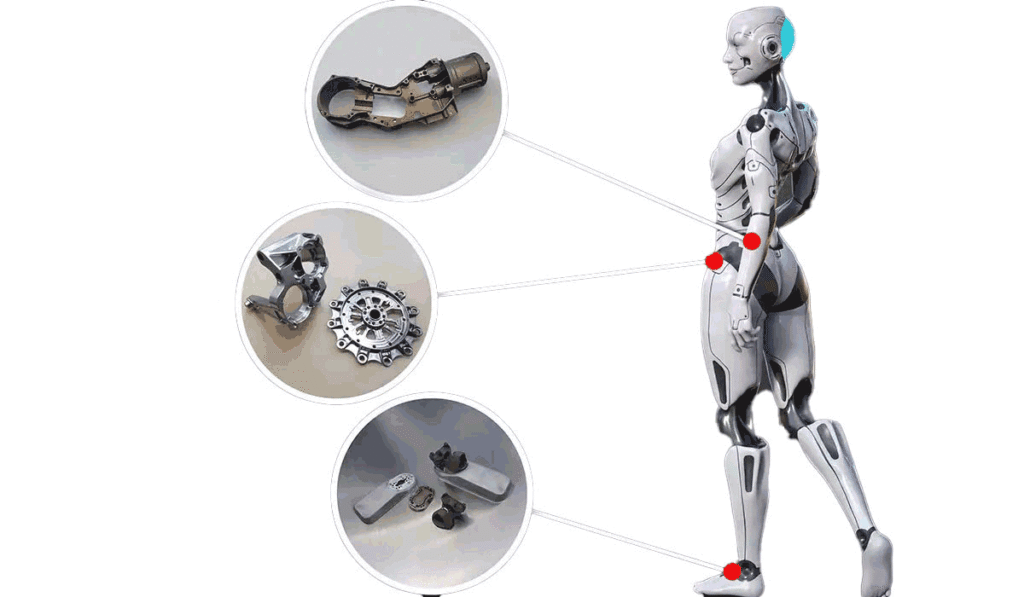
Humanoid robots represent the highest level of mechanical sophistication in modern robotics. They replicate human motion, dexterity, perception systems, and physical functionality. Achieving this level of complexity requires extremely precise mechanical components—parts capable of meeting tight tolerances, complex geometries, lightweight requirements, high dynamic stability, and long-term reliability.
Precision CNC machining has therefore become the cornerstone manufacturing method for humanoid robot development. From skeletal frames and joint assemblies to sensor housings and custom actuation mechanisms, CNC machining enables the production of high-performance components that cannot be achieved through casting, stamping, or injection molding.
1. Introduction to Humanoid Robot Components
Humanoid robots are designed to simulate human physical structure and behavior. Their systems usually include:
- Head (with sensors, cameras, AI modules)
- Torso structure
- Shoulder, elbow, wrist joints
- Legs, hips, knees, ankles
- Hands and fingers with multi-axis micro-actuators
- Internal skeleton and support frames
These systems require complex mechanical parts such as:
✔ Multi-axis joint housings
✔ Servo and actuator mounts
✔ Complex linkages
✔ Precision gear trains
✔ Structural frameworks
✔ Thermal and sensor housings
✔ Lightweight yet high-strength exoskeleton plates
Because of these intricate requirements, precision CNC machining becomes indispensable for achieving the necessary mechanical performance.
2. Why Precision CNC Machining Is Essential for Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots demand components that are:
- mechanically strong
- lightweight
- highly accurate
- tolerant of repeated dynamic loads
- compatible with servo control precision
- capable of holding complex internal routing (wiring, sensors)
CNC machining fulfills these requirements due to:
2.1 Ultra-high accuracy
Up to ±0.005 mm tolerances allow seamless motion control.
2.2 Ability to produce highly complex geometries
5-axis CNC machines can manufacture:
- anatomical joint shapes
- curved skeletal structures
- hollow internal channels
- asymmetric mechanical housings
2.3 Excellent repeatability
Critical for batch production of robotic components.
2.4 Compatibility with advanced materials
CNC machines process:
- aerospace aluminum
- titanium
- high-strength steels
- engineering plastics
2.5 Superior mechanical performance
Machined parts retain material integrity, ensuring:
- strength
- stability
- fatigue resistance
For humanoid robots, where every millimeter affects movement accuracy, CNC machining is the gold standard.
3. Key Humanoid Robot Components Manufactured With Precision CNC Machining
Here are the primary components typically produced via CNC machining in humanoid robot systems.
3.1 Structural Frames & Exoskeleton Elements
Humanoid robots require rigid yet lightweight frames:
- aluminum skeleton structures
- lightweight rib reinforcements
- torso and pelvic frames
- exoskeleton protective plates
CNC machining ensures a high stiffness-to-weight ratio.
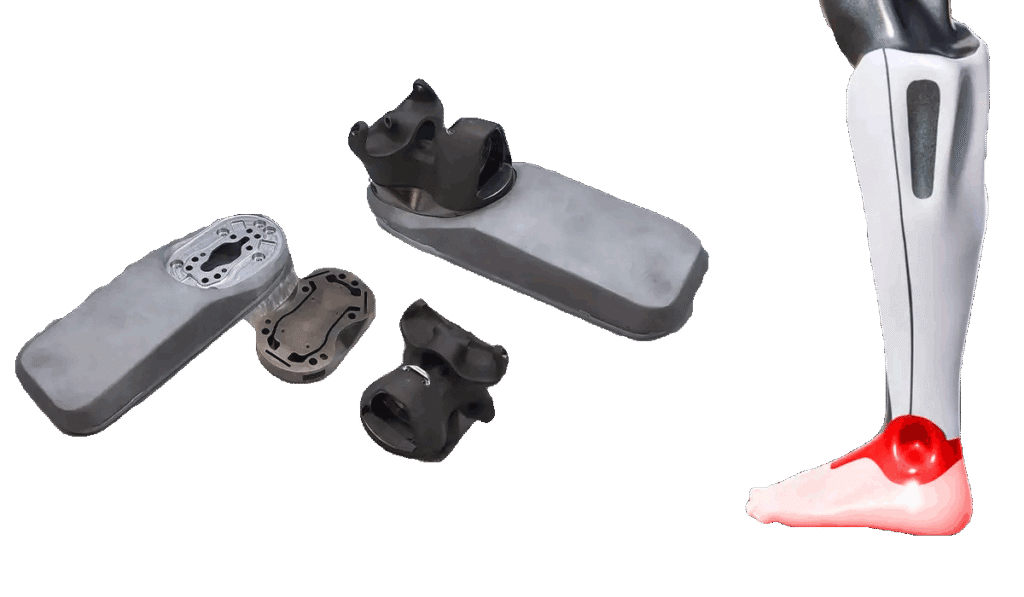
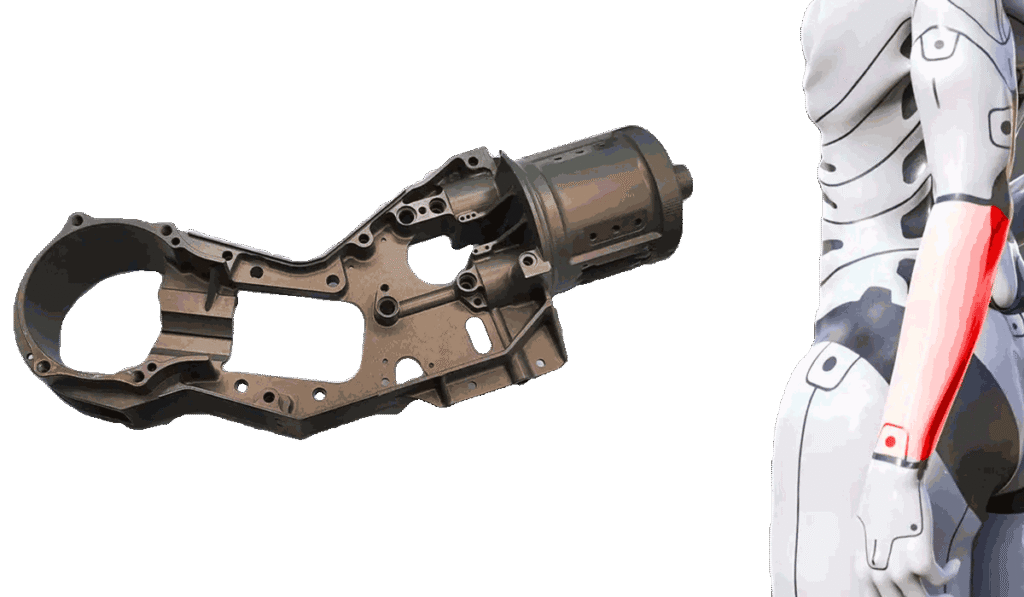
3.2 Joint Housings and Multi-Axis Assemblies
Joint mechanisms replicate natural human motion:
- shoulder ball-and-socket assemblies
- knee hinge systems
- wrist rotational clusters
- neck yaw-pitch-roll units
CNC machining ensures:
- tight bearing fit
- smooth motion
- strong load-bearing capabilities
3.3 Gears, Transmission Parts & Harmonic Drive Housings
Precision motion control relies on:
- gearboxes
- custom spur & planetary gears
- harmonic drive housings
- timing pulleys and shafts
CNC machining ensures micron-level accuracy.
3.4 Sensor, Camera & Lidar Housings
Humanoid robots integrate:
- 3D vision modules
- depth cameras
- Lidar sensors
- infrared and ultrasonic sensors
CNC allows:
- integrated cooling channels
- thin-wall construction
- internal mounting bosses
3.5 End Effectors: Robotic Hands & Fingers
These are among the most complex components.
CNC machining allows fabrication of:
- finger segments
- micro hinge mechanics
- actuator mounts
- tendon routing channels
Precision alignment is critical for dexterous movement.
3.6 Actuator Brackets & Motor Mounts
Essential to maintain precise alignment.
CNC machining ensures:
- vibration stability
- precise shaft alignment
- compatible tolerances with servo drives
4. CNC Machining Processes Used in Humanoid Robot Component Manufacturing
To meet the complexity and precision demands, manufacturers use a combination of CNC techniques.
4.1 5-Axis CNC Milling
Best for:
- complex joint housings
- curved skeletal shapes
- aerodynamic covers
- multi-angle surfaces
5-axis milling eliminates multiple setups and maintains precision.
4.2 CNC Turning
Used for cylindrical parts:
- shafts
- bushings
- joint pins
- harmonic drive bodies
4.3 Swiss CNC Turning
Ideal for very small precision parts:
- micro gear shafts
- finger actuation pins
- hollow miniature tubes
4.4 EDM Machining (Wire and Sink EDM)
Used for:
- ultra-hard metals
- tight internal corners
- miniature gear teeth
4.5 CNC Drilling & Deep Hole Drilling
Needed for wiring channels in structural limbs and torsos.
4.6 Hybrid CNC + Additive Manufacturing
For extremely complex internal routing, hybrid manufacturing creates:
- lattice reinforcement
- lightweight skeletons
- topology-optimized components
5. Materials Used in Precision Humanoid Robot CNC Components
Materials are selected for strength-to-weight, stiffness, thermal stability, and fatigue resistance.
5.1 Aluminum Alloys (6061, 7075, 2024)
Used for:
- exoskeleton
- internal frames
- joints
- brackets
Benefits:
- lightweight
- strong
- corrosion-resistant
- excellent machinability
5.2 Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V)
Used for high-load areas:
- knee and hip joints
- torque-heavy mounts
- critical structural parts
Benefits:
- extremely strong
- lightweight
- fatigue-resistant
5.3 Stainless Steel (304, 316, 17-4 PH)
Used for:
- gears
- shafts
- bearings housing
5.4 Engineering Plastics
Such as:
- POM
- PC
- Nylon
- Peek
Used for:
- covers
- insulators
- lightweight components
6. Tolerance Requirements for Humanoid Robot CNC Parts
Typical tolerances include:
±0.005–0.01 mm
for bearing fits, joints, and actuator mounts
±0.02–0.05 mm
for structural frames
±0.001–0.003 mm
for miniature gears and medical-grade fingers
Robotics tolerances are among the most demanding in the machining industry.
7. Manufacturing Challenges & How CNC Solves Them
7.1 Complex Multi-Axis Joint Geometry
Humanoid joints require human-like movement.
5-axis machining solves:
- compound curves
- undercuts
- spherical geometries
7.2 Lightweight but Strong Structures
CNC allows:
- thin walls
- internal pockets
- topology-optimized shapes
7.3 Heat Management
Sensor housings require:
- thermal channels
- heat-dissipation fins
CNC makes these easily.
7.4 Tight Fit Between Moving Parts
CNC guarantees:
- accurate bearing seats
- precise shaft alignment
- smooth motion
8. Surface Finishing for Robot Components
Common finishes include:
- anodizing
- bead blasting
- hard coat
- electropolishing
- nickel plating
- powder coating
These improve:
- friction
- corrosion resistance
- aesthetics
- durability
9. Cost Drivers in CNC Machining for Robotics
Key factors include:
- material type
- complexity
- 5-axis machine time
- tolerances
- surface finish
- batch volume
High complexity → higher cost.
But precision is essential for humanoid robot performance.
10. Case Studies: CNC Components in Modern Humanoid Robots
10.1 Tesla Optimus
Uses CNC components for:
- lightweight arm structures
- joint housings
- actuator frames
10.2 Boston Dynamics Atlas
CNC parts ensure:
- high-impact resistance
- dynamic joint motion
10.3 Agility Robotics Digit
CNC-machined legs and joints provide stability for bipedal operation.
11. Future Trends in CNC Machining for Humanoid Robots
- hybrid CNC + AM
- carbon fiber + CNC integration
- lightweight titanium alloys
- AI-driven CAM optimization
- Higher tolerance micro-machining
Conclusion
Precision CNC machining is the foundation of modern humanoid robot development. Its ability to produce ultra-accurate, lightweight, and complex components makes it the most essential manufacturing technology for advanced robotics. As humanoid robots continue evolving toward real-world deployment—manufacturing, healthcare, service, and logistics—precision CNC machining will become increasingly vital to their performance and reliability.