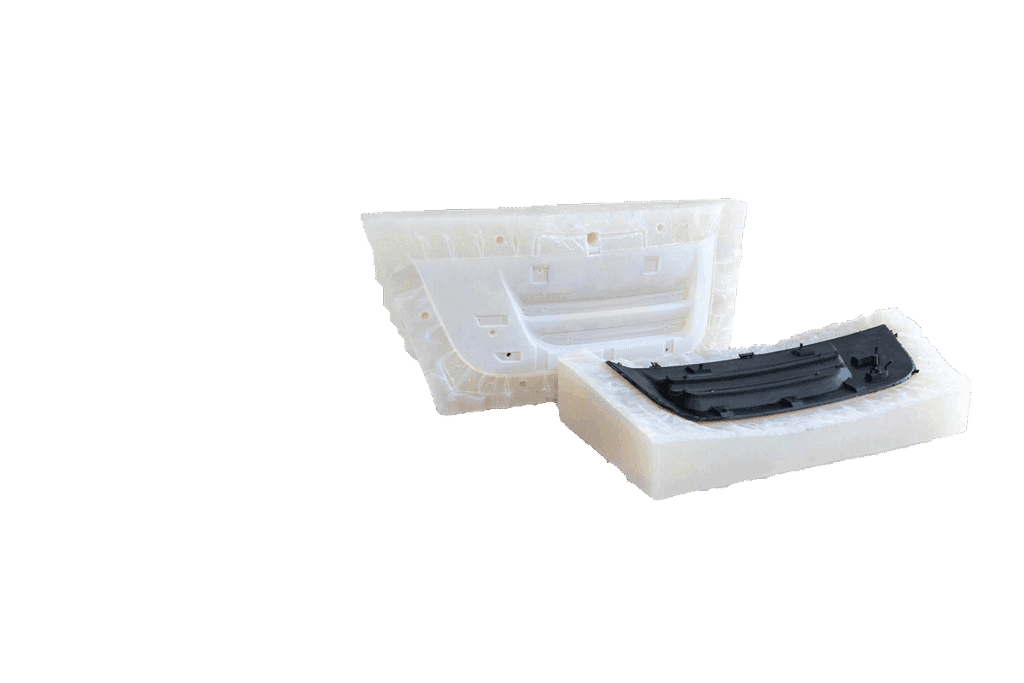
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, companies across industries need cost-effective solutions for creating prototypes and low-volume production parts. While traditional methods such as CNC machining and injection molding remain popular, vacuum casting services have emerged as a versatile alternative. This process bridges the gap between rapid prototyping and mass production, providing high-quality parts that replicate final products with remarkable accuracy.
Whether you are in automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, or medical device development, vacuum casting services offer a practical pathway to shorten lead times, reduce expenses, and ensure that product designs are validated before full-scale manufacturing begins. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of vacuum casting, its benefits, limitations, applications, and why it remains a preferred choice for businesses worldwide.
What Is Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting is a manufacturing technique used to produce small batches of high-quality plastic or rubber parts by utilizing silicone molds. The process is also referred to as urethane casting because it often involves the use of polyurethane resins. It is particularly well-suited for prototyping, design validation, and low-volume production runs where cost efficiency and speed are critical.
The core principle involves creating a master model (typically via CNC machining or 3D printing), from which a silicone mold is made. This mold is then used in a vacuum chamber to cast polyurethane resin under controlled conditions, eliminating air bubbles and ensuring precise detail reproduction. The result is a set of parts that closely resemble injection-molded components in terms of appearance, mechanical performance, and functionality.
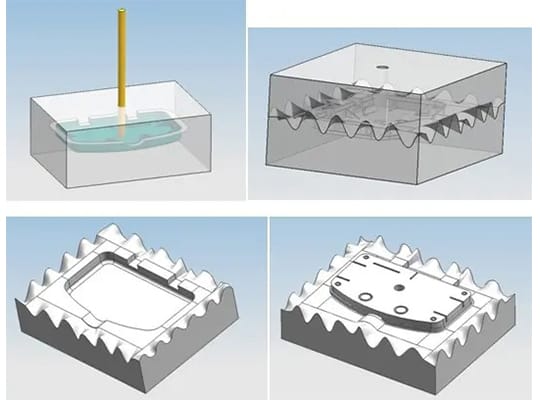
The Vacuum Casting Process Step by Step
The efficiency and reliability of vacuum casting services lie in their structured process. Here’s a detailed look at each stage:
1. Creating the Master Model
The process begins with a master model, which defines the geometry of the final part. Common methods for creating master patterns include:
- CNC machining: Offers high precision and excellent surface finish.
- 3D printing (SLA or SLS): Fast and cost-effective, suitable for complex geometries.
2. Silicone Mold Preparation
Liquid silicone is poured over the master model inside a casting box. Once cured, the mold is cut open carefully to release the master, leaving a cavity that replicates its shape.
3. Casting Under Vacuum
The chosen resin (polyurethane, elastomer, etc.) is mixed and poured into the silicone mold. The mold is placed inside a vacuum chamber to remove air bubbles and ensure consistent material density.
4. Curing Process
After filling, the mold is placed in an oven where the resin solidifies under controlled temperature. This ensures dimensional stability and mechanical integrity.
5. Demolding and Finishing
Once cured, the cast parts are removed from the mold. Additional post-processing, such as painting, polishing, or coating, may be applied depending on the project requirements.
This structured approach allows vacuum casting services to replicate highly detailed geometries and achieve surface finishes comparable to injection-molded parts.
Materials Used in Vacuum Casting
One of the strengths of vacuum casting lies in its versatility of materials. Providers of vacuum casting services typically offer a wide range of polyurethane resins designed to mimic the performance of production-grade plastics.
Common Material Options:
- Rigid Polyurethane Resins – mimic ABS, PC, or PMMA, offering strength and durability.
- Flexible Polyurethane Resins – replicate rubber-like materials such as TPE or silicone.
- Transparent Resins – used for clear parts like lenses or display covers.
- High-Temperature Resins – suitable for parts requiring thermal resistance.
- Elastomers – provide excellent flexibility and resilience for seals, gaskets, or functional prototypes.
By selecting the right resin, businesses can test designs that closely simulate the look, feel, and function of injection-molded parts, making vacuum casting services a practical choice for validation and testing.
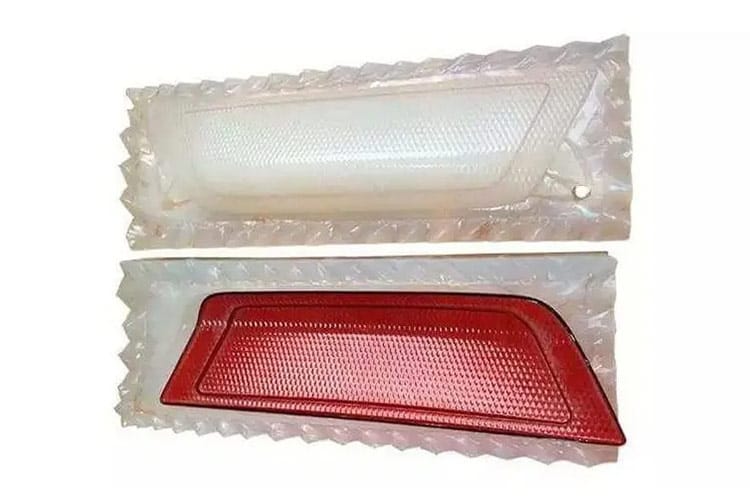

Advantages of Vacuum Casting Services
Vacuum casting has become increasingly popular because it offers several advantages over alternative prototyping and low-volume manufacturing methods.
1. Cost-Effective Production
Compared to injection molding, vacuum casting services require significantly lower tooling costs. Silicone molds are inexpensive and easy to produce, making them ideal for limited production runs.
2. High-Quality Parts
Parts produced through vacuum casting boast excellent surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and fine detail reproduction.
3. Versatility in Materials
With the ability to simulate plastics and elastomers, vacuum casting offers flexibility for diverse applications.
4. Rapid Turnaround
Lead times are typically much shorter than with traditional tooling, enabling companies to accelerate their product development cycles.
5. Small-Batch Efficiency
Vacuum casting services are optimized for quantities ranging from 5 to 100+ units, making them ideal for pre-series validation or market testing.

Limitations of Vacuum Casting
While vacuum casting services offer significant advantages, there are limitations to consider:
- Limited Production Volume: Not suitable for mass production due to mold lifespan (usually 20–25 casts per mold).
- Material Constraints: Properties may not perfectly match those of production-grade plastics.
- Dimensional Shrinkage: Slight shrinkage (0.2–0.3%) may occur during curing.
- Labor-Intensive: Post-processing may increase costs for highly detailed parts.
Understanding these limitations helps businesses decide when vacuum casting is the most appropriate solution.
Vacuum Casting vs. Other Manufacturing Processes
When evaluating vacuum casting services, it’s important to compare them with other popular prototyping and manufacturing techniques.
Vacuum Casting vs. CNC Machining
- CNC machining excels in precision and durability but is less cost-effective for complex geometries.
- Vacuum casting allows faster replication of intricate parts at a lower cost.
Vacuum Casting vs. 3D Printing
- 3D printing is great for rapid prototypes, but lacks the surface finish and material variety of vacuum casting.
- Vacuum casting services produce parts with better aesthetics and functionality.
Vacuum Casting vs. Injection Molding
- Injection molding is ideal for large-scale production but has high upfront tooling costs.
- Vacuum casting offers an affordable option for low-volume runs without expensive steel molds.
Applications of Vacuum Casting Services
Vacuum casting services are widely adopted across industries due to their adaptability.
Automotive
- Functional prototypes of interior and exterior components.
- Small-batch production for custom car parts.
Aerospace
- Cabin interior prototypes.
- Low-volume production of specialty tools or equipment housings.
Medical Devices
- Prototyping enclosures for diagnostic equipment.
- Biocompatible part validation.
Consumer Electronics
- Casings for smartphones, tablets, and wearables.
- Transparent display covers.
Industrial Equipment
- Rubber seals, connectors, and protective covers.
These applications demonstrate how vacuum casting supports both design validation and real-world functionality testing.
How to Choose the Right Vacuum Casting Services Provider
Selecting the right partner for vacuum casting services is crucial for achieving reliable results. Consider the following factors:
- Experience and Expertise: Look for companies with proven track records in vacuum casting.
- Material Options: Ensure they offer a wide selection of resins to meet your needs.
- Quality Standards: Check for ISO certifications or compliance with industry standards.
- Lead Times: A good provider should deliver parts quickly without sacrificing quality.
- Value-Added Services: Post-processing, painting, and assembly support add extra value.
The Future of Vacuum Casting Technology
As manufacturing technology evolves, vacuum casting services continue to advance. Improvements in resin formulations, mold-making techniques, and automation are extending the lifespan of silicone molds and enhancing part performance. Additionally, the integration of vacuum casting with digital manufacturing workflows (such as CAD-CAM and AI-driven design validation) is further streamlining the process.
Looking ahead, vacuum casting will remain a critical bridge between rapid prototyping and full-scale production, supporting industries that require precision, speed, and flexibility.
Conclusion
Vacuum casting services represent a powerful solution for companies seeking cost-effective, high-quality prototypes and low-volume production parts. With its ability to replicate fine details, provide versatile material choices, and deliver rapid results, vacuum casting continues to be a preferred choice for engineers, designers, and manufacturers alike.
By understanding the process, materials, advantages, and limitations, businesses can make informed decisions about when and how to leverage vacuum casting in their product development cycles. Whether for automotive, aerospace, medical, or consumer electronics applications, vacuum casting services remain an indispensable tool in modern manufacturing.