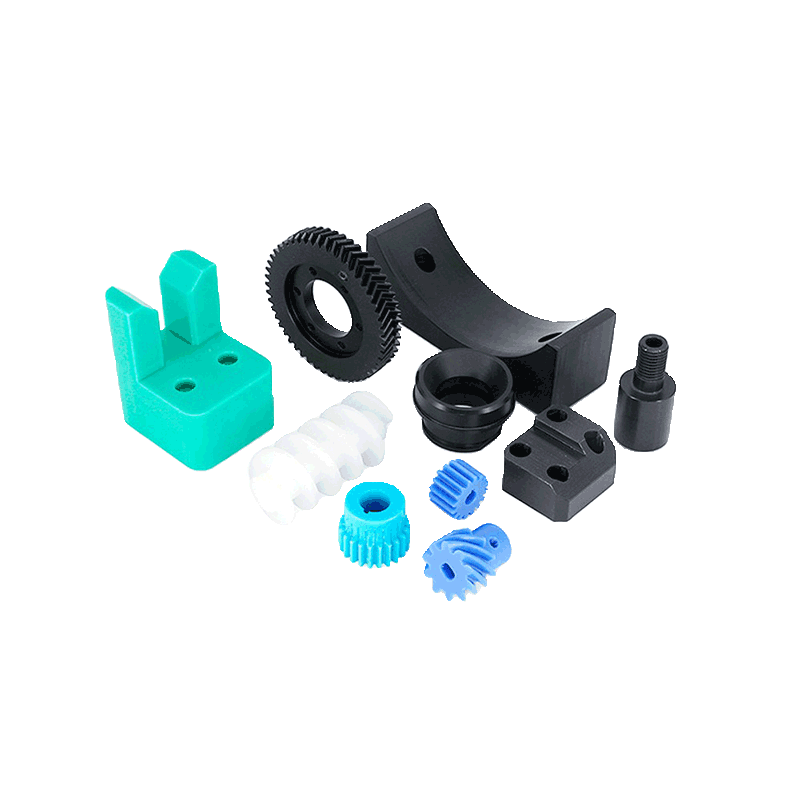
Introduction to Plastic CNC-Machined Parts
Plastic CNC-machined parts are essential across industries that demand precision, stability, and lightweight performance. Unlike metals, plastics offer unique advantages such as corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, reduced weight, and the ability to maintain tight tolerances without complex processing. With the advancement of CNC plastic machining, manufacturers can now achieve high repeatability and accuracy, producing end-use parts, prototypes, and functional components for aerospace, medical, automotive, robotics, electronics, and consumer products.
The demand for high-quality plastic CNC-machined parts is growing because companies need fast turnaround, high accuracy, and the ability to iterate designs without investing in tooling. CNC plastic machining eliminates mold costs and supports both rapid prototyping and low-volume production.
This guide explains everything you need to know about plastic CNC-machined parts — from materials and machining techniques, to surface finishing, tolerances, inspection, applications, and manufacturing best practices.
2. What Are Plastic CNC-Machined Parts?
Plastic CNC-machined parts are components manufactured using subtractive machining processes—typically CNC milling, CNC turning, drilling, or routing—on engineered plastic materials. CNC machining uses automated, computer-controlled tools to remove material from plastic stock.
Key characteristics of CNC plastic machined parts include:
- High precision and tight tolerances
- Consistent dimensions and repeatability
- No tooling or mold cost
- Suitable for low to medium volume production
- Wide material selection, including engineering-grade plastics
- Excellent surface finish
Common uses:
- Enclosures
- Mechanical components
- Gears and pulleys
- Custom brackets
- Insulating parts
- Medical device components
- Fixtures and jigs
- Robotic parts
CNC machining is ideal for plastics, where injection molding might be too costly for small batches or where prototypes must match the final product’s mechanical performance.
3. Advantages of CNC Plastic Machining
3.1 High-Dimensional Accuracy
Plastic CNC-machined parts can reach tolerances of ±0.02 mm depending on material stability. This precision is essential for medical instruments, aerospace components, optical housings, and robotics.
3.2 No Molding Cost
Injection molding requires expensive steel or aluminum molds. CNC machining has zero tooling, making it ideal for prototypes and small-volume production.
3.3 Wide Material Flexibility
CNC machining supports more types of plastics than molding can handle. It works well with high-performance materials such as PEEK, PTFE, and Ultem.
3.4 Fast Turnaround Time
CNC machining can deliver parts within hours to days. This makes it ideal for rapid prototyping and engineering validation tests (EVT/DVT).
3.5 Better Mechanical Properties
CNC plastic parts have no molding flow lines, weld marks, or internal stresses caused by injection molding cooling. The material’s natural strength and stability remain intact.
3.6 Excellent Surface Finish
CNC machining can achieve smooth, aesthetic surfaces suitable for end-use components.
3.7 Easy Customization
Modifying a CNC part requires only program adjustments—not mold changes—making design changes fast and inexpensive.
4. Common Materials Used in CNC Plastic Machining
Choosing the correct plastic material is crucial to achieving the desired performance. Here are the most common materials used in plastic CNC-machined parts:
4.1 ABS
- Lightweight
- Good toughness
- Easy to machine
- Low cost
- Applications: prototypes, casings, consumer product components
4.2 Polycarbonate (PC)
- High impact resistance
- Good dimensional stability
- Transparent option
- Applications: lenses, safety housings, medical components
4.3 Acrylic (PMMA)
- Excellent transparency
- Good surface finish
- Scratch-resistant
- Applications: lighting covers, display components
4.4 Nylon (PA6 / PA66)
- High mechanical strength
- Good wear resistance
- Low friction
- Applications: gears, bushings, mechanical parts
4.5 POM (Delrin / Acetal)
- High-dimensional stability
- Excellent machinability
- Low moisture absorption
- Applications: precision bearings, rollers, automotive parts
4.6 PTFE (Teflon)
- Chemical resistance
- Low friction
- High temperature tolerance
- Applications: seals, gaskets, insulating components
4.7 PEEK
- High-performance engineering plastic
- Very stable
- Excellent mechanical properties
- Applications: aerospace, medical implants, semiconductor components
4.8 Ultem (PEI)
- High heat resistance
- Good strength-to-weight ratio
- Applications: medical, aerospace, electronics
4.9 HDPE / LDPE
- Lightweight
- Impact-resistant
- Applications: tanks, industrial components
4.10 PVC
- Corrosion resistance
- Good electrical insulation
- Applications: fluid handling components, electrical parts
5. CNC Processes Used for Plastic Machining
5.1 CNC Milling
The most common process for making 3D plastic parts with pockets, slots, curves, chamfers, and complex geometries.
5.2 CNC Turning
Used for cylindrical parts such as bushings, rollers, pulleys, and rings.
5.3 Drilling
For precise holes, ports, and threaded features.
5.4 Routing
Used for large plastic sheets or panel components.
5.5 Multi-Axis Machining
5-axis CNC machining is ideal for complex and organic shapes, used in medical, robotics, and aerospace industries.
6. Design Considerations for Plastic CNC-Machined Parts
To optimize your design for CNC plastic machining, consider the following:
6.1 Wall Thickness
Avoid extremely thin walls. Recommended minimum: 1.0–1.5 mm.
6.2 Avoid Sharp Internal Corners
Use fillets to reduce machining difficulty and stress concentration.
6.3 Tolerance Selection
Plastics move more under heat and pressure than metals. Typical range: ±0.05–0.1 mm for many plastics.
6.4 Thread Design
Prefer inserts (e.g., brass threaded inserts) for improved strength.
6.5 Avoid Heat Buildup
Sharp tools and slower feed speeds are necessary to prevent melting.
6.6 Chamfers and Radii
Use chamfers for edges to prevent cracking.
6.7 Moisture Absorption
Materials like Nylon change dimensions when absorbing moisture.
7. Surface Finishing Options for Plastic CNC-Machined Parts
- As-milled finish
- Polishing (e.g., for acrylic or PC)
- Bead blasting for matte finish
- Painting or coating
- Laser engraving
- Anodizing-like effects (for certain plastics only)
8. Typical Tolerances for CNC Plastic Machining
Plastic tolerances differ from metals because plastics expand with heat and shrink with humidity.
MaterialTypical ToleranceNotes
ABS ±0.1 mm Easy to machine
PC ±0.05–0.1 mm Very stable
Nylon ±0.2 mm Absorbs moisture
POM ±0.05 mm Best precision
PEEK ±0.02–0.05 mm High performance
9. Inspection and Quality Control
For precision plastic parts, manufacturers commonly use:
- Digital calipers & micrometers
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
- Optical comparators
- Height gauges
- Thread gauges
- Surface roughness testers
Quality control ensures that CNC-machined plastic parts meet engineering requirements and functional fit.
10. Applications of Plastic CNC Machined Parts
10.1 Medical Industry
- Surgical components
- Device housings
- Diagnostic equipment parts
- Sterilization trays
10.2 Electronics
- Insulators
- Connectors
- Sensor housings
- Enclosures
10.3 Robotics & Automation
- Structural components
- Gears and pulleys
- End-effectors
- Lightweight precision parts
10.4 Aerospace
- Interior components
- Insulation blocks
- Lightweight custom parts
10.5 Automotive
- Prototypes for testing
- Custom brackets
- Wear components
10.6 Consumer Products
- Prototype casings
- Functional mechanical parts
- Small batch production
11. Comparing CNC Plastic Machining vs. Injection Molding
FeatureCNC MachiningInjection Molding
Tooling Cost None Very high
Lead Time Hours–days Weeks–months
Volume Low–medium Medium–high
Material Strength Higher (no weld lines) Good, depends on mold
Tolerances Excellent Good
Design Flexibility: Very high, Limited after mold creation
Best choice for prototypes, custom parts, and small runs: CNC
Best choice for mass production: injection molding
12. How to Choose a Reliable CNC Plastic Machining Supplier
Look for:
- Experience with engineering plastics
- Ability to achieve tight tolerances
- High-performance machining equipment
- 5-axis capabilities
- Strong QC team
- Fast quoting and DFM support
- Good communication and engineering response time
13. Conclusion
Plastic CNC-machined parts play a crucial role in modern manufacturing. With excellent precision, fast turnaround, consistent quality, and unmatched flexibility, CNC plastic machining is the top choice for prototypes, engineering validation, and low- to mid-volume production. As industries adopt more lightweight and high-performance materials, CNC machining will remain one of the most important manufacturing options.
Whether you are designing prototypes, functional parts, or high-precision components, understanding materials, tolerances, machining methods, and design rules ensures you achieve the best results in cost, quality, and performance.
